Note
Click here to download the full example code
Compute Graph properties from a given connectivity matrix¶
The conmat_to_graph pipeline performs graph analysis .
The input data should be a symetrical connecivity matrix in npy format.
# Authors: David Meunier <david_meunier_79@hotmail.fr>
# License: BSD (3-clause)
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
import os.path as op
import nipype.pipeline.engine as pe
from nipype.interfaces.utility import IdentityInterface
import nipype.interfaces.io as nio
Check if data are available
from graphpype.utils_tests import load_test_data
data_path = load_test_data("data_con_meg")
This will be what we will loop on
freq_band_names = ['alpha', 'beta']
Then, we create our workflow and specify the base_dir which tells nipype the directory in which to store the outputs.
# workflow directory within the `base_dir`
graph_analysis_name = 'graph_analysis'
main_workflow = pe.Workflow(name=graph_analysis_name)
main_workflow.base_dir = data_path
Then we create a node to pass input filenames to DataGrabber from nipype
infosource = pe.Node(
interface=IdentityInterface(fields=['freq_band_name']),
name="infosource")
infosource.iterables = [('freq_band_name', freq_band_names)]
and a node to grab data. The template_args in this node iterate upon the values in the infosource node
# template_path = '*%s/conmat_0_coh.npy'
# template_args = [['freq_band_name']
# datasource = create_datagrabber(data_path, template_path, template_args)
datasource = pe.Node(
interface=nio.DataGrabber(infields=['freq_band_name'],
outfields=['conmat_file']),
name='datasource')
datasource.inputs.base_directory = data_path
datasource.inputs.template = ("%s/conmat_0_coh.npy")
datasource.inputs.template_args = dict(
conmat_file=[['freq_band_name']])
datasource.inputs.sort_filelist = True
This parameter corrdesponds to the percentage of highest connections retains for the analyses. con_den = 1.0 means a fully connected graphs (all edges are present)
import json # noqa
import pprint # noqa
data_graph = json.load(open(op.join(op.dirname("__file__"),
"params_graph.json")))
pprint.pprint({'graph parameters': data_graph})
# density of the threshold
con_den = data_graph['con_den']
# The optimisation sequence
radatools_optim = data_graph['radatools_optim']
Out:
{'graph parameters': {'con_den': 0.05, 'radatools_optim': 'WN tfrf 100'}}
see http://deim.urv.cat/~sergio.gomez/download.php?f=radatools-5.0-README.txt for more details, but very briefly:
- WN for weighted unsigned (typically coherence, pli, etc.) and WS for signed (e.g. Pearson correlation)
- the optimisation sequence, can be used in different order. The sequence tfrf is proposed in radatools, and means: t = tabu search , f = fast algorithm, r = reposition algorithm and f = fast algorithm (again)
- the last number is the number of repetitions of the algorithm, out of which the best one is chosen. The higher the number of repetitions, the higher the chance to reach the global maximum, but also the longer the computation takes. For testing, 1 is admissible, but it is expected to have at least 100 is required for reliable results
The graph pipeline contains several nodes, some are based on radatools In particular, the two nodes are:
ephypype.interfaces.mne.spectral.SpectralConncomputes spectral connectivity in a given frequency bandsephypype.interfaces.mne.spectral.PlotSpectralConnplot connectivity matrix using the spectral_connectivity function function
# In particular, the two nodes are:
#
# * :class:`ephypype.interfaces.mne.spectral.SpectralConn` computes spectral
# connectivity in a given frequency bands
# * :class:`ephypype.interfaces.mne.spectral.PlotSpectralConn` plot
# connectivity matrix using the |plot_connectivity_circle| function
# .. |plot_connectivity_circle| raw:: html
# <a href="http://martinos.org/mne/stable/generated/mne.viz.
# plot_connectivity_circle .html#mne.viz.plot_connectivity_circle"
# target="_blank">spectral_connectivity function</a>
from graphpype.pipelines import create_pipeline_conmat_to_graph_density
graph_workflow = create_pipeline_conmat_to_graph_density(
data_path, con_den=con_den, optim_seq=radatools_optim)
We then connect the nodes two at a time. We connect the output of the infosource node to the datasource node. So, these two nodes taken together can grab data.
main_workflow.connect(infosource, 'freq_band_name',
datasource, 'freq_band_name')
main_workflow.connect(datasource, 'conmat_file',
graph_workflow, "inputnode.conmat_file")
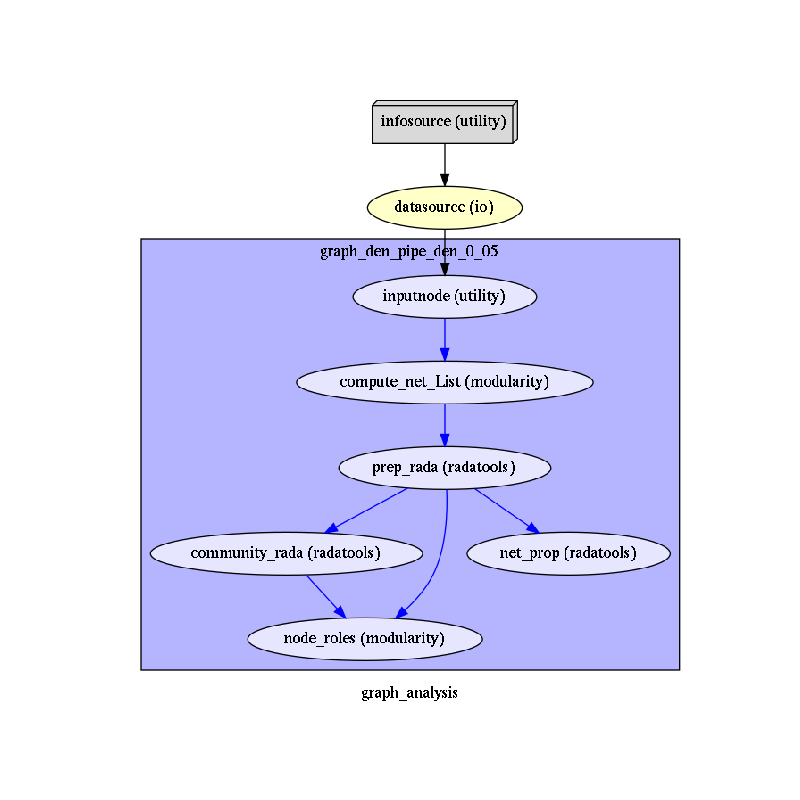
To do so, we first write the workflow graph (optional)
main_workflow.write_graph(graph2use='colored') # colored
and visualize it. Take a moment to pause and notice how the connections here correspond to how we connected the nodes.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # noqa
img = plt.imread(op.join(data_path, graph_analysis_name, 'graph.png'))
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
Finally, we are now ready to execute our workflow.
main_workflow.config['execution'] = {'remove_unnecessary_outputs': 'false'}
# Run workflow locally on 2 CPUs
main_workflow.run(plugin='MultiProc', plugin_args={'n_procs': 2})
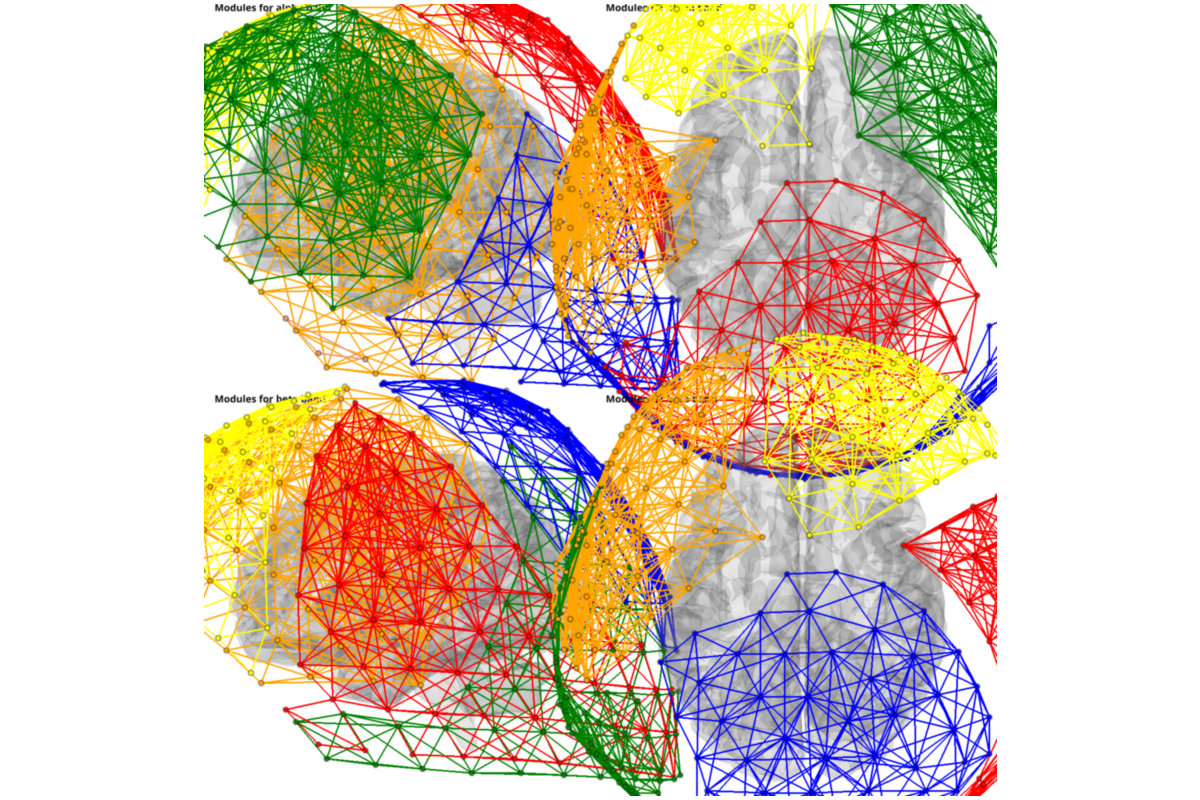
plotting
from graphpype.utils_visbrain import visu_graph_modules # noqa
labels_file = op.join(data_path, "correct_channel_names.txt")
coords_file = op.join(data_path, "MNI_coords.txt")
from visbrain.objects import SceneObj, BrainObj # noqa
sc = SceneObj(size=(1500, 1500), bgcolor=(1, 1, 1))
views = ['left','top']
for nf, freq_band_name in enumerate(freq_band_names):
res_path = op.join(
data_path, graph_analysis_name,
"graph_den_pipe_den_"+str(con_den).replace(".", "_"),
"_freq_band_name_"+freq_band_name)
lol_file = op.join(res_path, "community_rada", "Z_List.lol")
net_file = op.join(res_path, "prep_rada", "Z_List.net")
for i_v,view in enumerate(views):
b_obj = BrainObj("B1", translucent=True)
sc.add_to_subplot(
b_obj, row=nf, col = i_v, use_this_cam=True, rotate=view,
title=("Modules for {} band".format(freq_band_name)),
title_size=14, title_bold=True, title_color='black')
c_obj,s_obj = visu_graph_modules(
lol_file=lol_file, net_file=net_file, coords_file=coords_file, inter_modules=False, z_offset=+50)
sc.add_to_subplot(c_obj, col = i_v, row=nf)
sc.add_to_subplot(s_obj, col = i_v, row=nf)
sc.preview()
Total running time of the script: ( 5 minutes 40.799 seconds)