Note
Click here to download the full example code
01. Freesurfer anatomical pipeline¶
This workflow runs the Nipype Interface wrapping the recon-all command of Freesurfer.
The solution of MEG inverse problem requires knowledge of the lead field matrix. A cortical segmentation of the anatomical MRI is necessary to generate the source space, where the neural activity will be estimated. A Boundary Element Model (BEM) which uses the segmented surfaces is used to construct the lead field matrix.
To perform the cortical segmentation we provide a workflow based on nipype Interface wrapping the recon-all command of Freesurfer. The output of ReconAll Node node is used as input of another node that creates the BEM surfaces using the FreeSurfer watershed algorithm.
The workflow generates an HTML report displaying the BEM surfaces as colored contours overlaid on the T1 MRI images to verify that the surfaces do not intersect.
Warning
Make sure that Freesurfer is properly configured before running this script.
# Authors: Annalisa Pascarella <a.pascarella@iac.cnr.it>
# License: BSD (3-clause)
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 1
Import modules¶
import os
import json
import pprint
import os.path as op
import nipype.pipeline.engine as pe
from nipype.interfaces.freesurfer import ReconAll
from nipype.interfaces.utility import Function
from ephypype.nodes import create_iterator, create_datagrabber
from ephypype.compute_fwd_problem import _create_bem_sol
Define data and variables¶
Let us specify the variables that are specific for the data analysis (the
main directories where the data are stored, the list of subjects and
sessions, …) and the variable specific for the particular pipeline
(MRI path, Freesurfer fir, …) in a json file.
# Read experiment params as json
params = json.load(open("params.json"))
pprint.pprint({'parameters': params["general"]})
subjects_dir = params["general"]["subjects_dir"]
subject_ids = params["general"]["subject_ids"]
NJOBS = params["general"]["NJOBS"]
if "subjects_dir" in params["general"].keys():
data_path = params["general"]["subjects_dir"]
else:
data_path = os.path.expanduser("~")
# Check envoiroment variables
if not os.environ.get('FREESURFER_HOME'):
raise RuntimeError('FREESURFER_HOME environment variable not set')
os.environ["SUBJECTS_DIR"] = subjects_dir
print(f'SUBJECTS_DIR {os.environ["SUBJECTS_DIR"]} ')
Specify Nodes¶
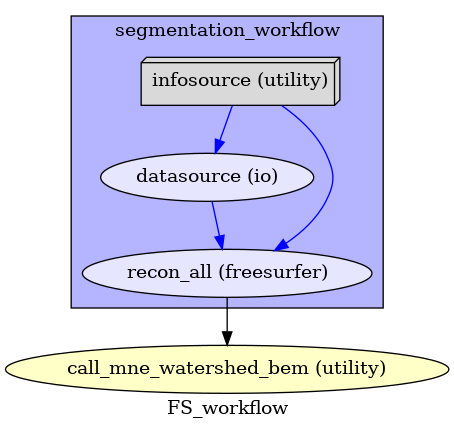
Infosource and Datasource¶
We create a node to pass input filenames and a node to grab data. The
template_args in this datasource node iterate upon
the values in the infosource node.
Here we define an input field for create_datagrabber called
subject_id. This is then used to set the template (see %s in the
template). We look for .nii files located in the ses-mri/anat folder of
the subject.
infosource = create_iterator(['subject_id'], [subject_ids])
template_path = '../%s/ses-mri/anat/%s*T1w.nii.gz'
template_args = [['subject_id', 'subject_id']]
infields = ['subject_id']
datasource = create_datagrabber(data_path, template_path, template_args,
infields=infields)
ReconAll Node¶
recon_all node calls the nipype Interface wrapping the recon-all function
of Freesurfer that generates surfaces and parcellations of structural
data from anatomical images of a subject.
recon_all = pe.Node(interface=ReconAll(), infields=['T1_files'],
name='recon_all')
recon_all.inputs.subjects_dir = subjects_dir
recon_all.inputs.directive = 'all'
BEM Node¶
Then, we define a node wrapping an ephypype function calling make_watershed_bem of MNE Python package for BEM generation
bem_generation = pe.Node(interface=Function(
input_names=['subjects_dir', 'sbj_id'], output_names=['sbj_id'],
function=_create_bem_sol), name='call_mne_watershed_bem')
bem_generation.inputs.subjects_dir = subjects_dir
Create workflows¶
First, we create a workflow containing the ReconAll Node and specify the
connections between all nodes (infosource, datasource and
recon_all).
# reconall_workflow will be a node of the main workflow
reconall_workflow_name = 'segmentation_workflow'
reconall_workflow = pe.Workflow(name=reconall_workflow_name)
reconall_workflow.base_dir = data_path
reconall_workflow.connect(infosource, 'subject_id', datasource, 'subject_id')
reconall_workflow.connect(infosource, 'subject_id', recon_all, 'subject_id')
reconall_workflow.connect(datasource, 'raw_file', recon_all, 'T1_files')
Then, we create the main workflow where we will connect the output of
reconall_workflow to the input of bem_generation node.
freesurfer_workflow_name = 'FS_workflow'
main_workflow = pe.Workflow(name=freesurfer_workflow_name)
main_workflow.base_dir = subjects_dir
main_workflow.connect(reconall_workflow, 'recon_all.subject_id',
bem_generation, 'sbj_id')
Run workflow¶
Execute the pipeline
The code above sets up all the necessary data structures and the connectivity
between the processes, but does not generate any output. To actually run the
analysis on the data the Run()
function needs to be called.
main_workflow.write_graph(graph2use='colored')
main_workflow.config['execution'] = {'remove_unnecessary_outputs': 'false'}
main_workflow.run(plugin='LegacyMultiProc', plugin_args={'n_procs': NJOBS})
Results¶
The output of this workflow is the cortical segmentation of the
structural data that we find in the subjects_dir and will be used in
03. Compute inverse solution
Note
The main advantage to use this workflow lies in the parallel processing provided by nipype engine, that allows segmenting the 19 MRI data in less than two days while processing a single MRI generally takes one day.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.000 seconds)