Note
Click here to download the full example code
03. Compute inverse solution¶
This workflow mainly calls the inverse solution pipeline performing source reconstruction starting from the cleaned raw data obtained by 02. Preprocess MEG data.
The first node of the workflow (Event Node) extracts the events from
stimulus channel STI101. The events are saved in the Event Node
directory. For each subject, the different runs are also concatenated in
one single raw file and saved in Event Node directory.
The input of this node are the different runs taken from the
preprocessing workflow directory, i.e. the cleaned
raw data created by 02. Preprocess MEG data.
In the Inverse solution Node the raw data are epoched accordingly to
events specified in json file and created in Event Node.
The evoked datasets are created by averaging the different conditions specified
in the json file. The estimated neural time series are reconstructed
by the evoked data for each condition by dSPM inverse method.
Finally, the source estimates obtained by the
Inverse solution Node are morphed to the fsaverage brain in the
Morphing Node.
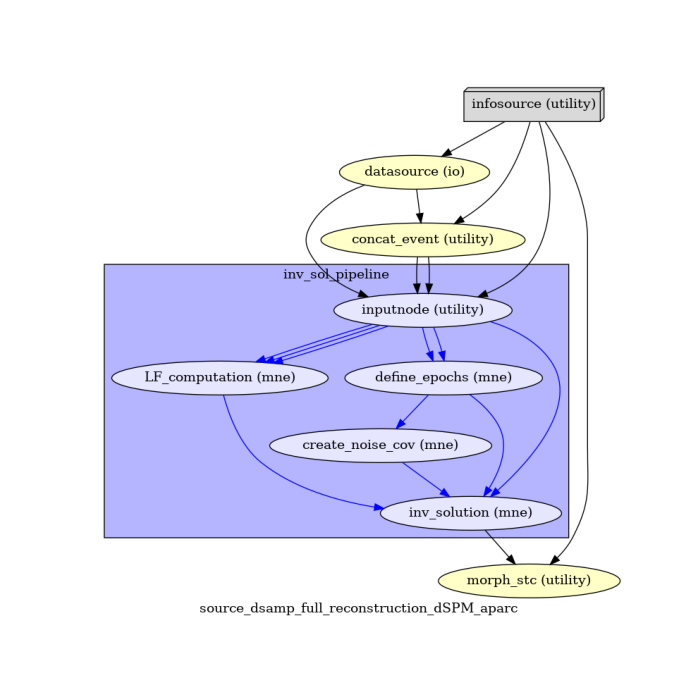
An overview of the workflow, its nodes and connections is given by the Workflow graph.
Warning
Before running this pipeline, the coregistration between the MRI and MEG device needs to be performed. It is reccomened to look at the MNE tutorial
# Authors: Annalisa Pascarella <a.pascarella@iac.cnr.it>
# License: BSD (3-clause)
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 1
Import modules¶
import os.path as op
import json
import pprint # noqa
import nipype.pipeline.engine as pe
from nipype.interfaces.utility import Function
from ephypype.nodes import create_iterator, create_datagrabber
from ephypype.pipelines.fif_to_inv_sol import create_pipeline_source_reconstruction # noqa
Define data and variables¶
Let us specify the variables that are specific for the data analysis (the
main directories where the data are stored, the list of subjects and
sessions, …) and the variable specific for the inverse pipeline
(events_id, inverse method, …) in a json file
params = json.load(open("params.json"))
pprint.pprint({'parameters': params["general"]})
data_type = params["general"]["data_type"]
subject_ids = params["general"]["subject_ids"]
NJOBS = params["general"]["NJOBS"]
session_ids = params["general"]["session_ids"]
subjects_dir = params["general"]["subjects_dir"]
is_short = params["general"]["short"] # to analyze a shorter segment of data
if "data_path" in params["general"].keys():
data_path = params["general"]["data_path"]
else:
data_path = op.expanduser("~")
print("data_path : %s" % data_path)
# source reconstruction
pprint.pprint({'inverse parameters': params["inverse"]})
events_id = params["inverse"]['events_id']
condition = params["inverse"]['condition']
new_name_condition = params["inverse"]["new_name_condition"]
t_min = params["inverse"]['tmin']
t_max = params["inverse"]['tmax']
spacing = params["inverse"]['spacing'] # oct-6
snr = params["inverse"]['snr']
inv_method = params["inverse"]['method'] # dSPM
parc = params["inverse"]['parcellation'] # aparc
trans_fname = op.join(data_path, params["inverse"]['trans_fname'])
{'parameters': {'NJOBS': 1,
'data_path': '/home/pasca/Science/workshop/PracticalMEEG/ds000117/derivatives/meg_derivatives',
'data_type': 'fif',
'session_ids': ['01', '02'],
'short': False,
'subject_ids': ['sub-01'],
'subjects_dir': '/home/pasca/Science/workshop/PracticalMEEG/ds000117/FSF'}}
data_path : /home/pasca/Science/workshop/PracticalMEEG/ds000117/derivatives/meg_derivatives
{'inverse parameters': {'condition': ['face/famous',
'scrambled',
'face/unfamiliar'],
'events_id': {'face/famous/first': 5,
'face/famous/immediate': 6,
'face/famous/long': 7,
'face/unfamiliar/first': 13,
'face/unfamiliar/immediate': 14,
'face/unfamiliar/long': 15,
'scrambled/first': 17,
'scrambled/immediate': 18,
'scrambled/long': 19},
'method': 'dSPM',
'new_name_condition': ['famous',
'scrambled',
'unfamiliar'],
'parcellation': 'aparc',
'snr': 3.0,
'spacing': 'oct-6',
'tmax': 1.0,
'tmin': -0.2,
'trans_fname': '*-trans.fif'}}
Define functions¶
Here we define two different functions that will be encapsulated in two
different nodes (Event Node and Morphing Node).
The run_events_concatenate function extracts events from the stimulus
channel while the compute_morph_stc morphs the source estimates obtained by
the Inverse solution Node into the fsaverage brain.
def run_events_concatenate(list_ica_files, subject):
'''
The events are extracted from stim channel 'STI101'. The events are saved
to the Node directory.
For each subject, the different runs are concatenated in one single raw
file and saved in the Node directory. We take the different runs from the
preprocessing workflow directory, i.e. the cleaned raw data.
'''
print(subject, list_ica_files)
import os
import mne
mask = 4096 + 256 # mask for excluding high order bits
delay_item = 0.0345
min_duration = 0.015
print(f"processing subject: {subject}")
raw_list = list()
events_list = list()
fname_events_files = []
print(" Loading raw data")
for i, run_fname in enumerate(list_ica_files):
run = i + 1
raw = mne.io.read_raw_fif(run_fname, preload=True)
events = mne.find_events(raw, stim_channel='STI101',
consecutive='increasing', mask=mask,
mask_type='not_and',
min_duration=min_duration)
print(f" S {subject} - {run} %s")
fname_events = os.path.abspath(f'run_{run:02d}-eve.fif')
mne.write_events(fname_events, events)
fname_events_files.append(fname_events)
delay = int(round(delay_item * raw.info['sfreq']))
events[:, 0] = events[:, 0] + delay
events_list.append(events)
raw_list.append(raw)
raw, events = mne.concatenate_raws(raw_list, events_list=events_list)
raw.set_eeg_reference(projection=True)
raw_file = os.path.abspath(f'{subject}_sss_filt_dsamp_ica-raw.fif')
print(raw_file)
raw.save(raw_file, overwrite=True)
event_file = os.path.abspath(f'{subject}_sss_filt_dsamp_ica-raw-eve.fif')
mne.write_events(event_file, events)
del raw_list
del raw
return raw_file, event_file, fname_events_files
def compute_morph_stc(subject, conditions, cond_files, subjects_dir):
import os.path as op
import mne
print(f"processing subject: {subject}")
# Morph STCs
stc_morphed_files = []
for k, cond_file in enumerate(cond_files):
print(conditions[k])
print(cond_file)
stc = mne.read_source_estimate(cond_file)
morph = mne.compute_source_morph(
stc, subject_from=subject, subject_to='fsaverage',
subjects_dir=subjects_dir)
stc_morphed = morph.apply(stc)
stc_morphed_file = op.abspath('mne_dSPM_inverse_morph-%s' % (conditions[k])) # noqa
stc_morphed.save(stc_morphed_file)
stc_morphed_files.append(stc_morphed_file)
return stc_morphed_files
def show_files(files):
print(files)
return files
Specify Nodes¶
Infosource and Datasource¶
We create an infosurce node to pass input filenames to the datasource
node to grab the data.
infosource = create_iterator(['subject_id'], [subject_ids])
We set the dir from which to get the preprocessed MEG data
preproc_wf_name = 'preprocessing_dsamp_short_workflow' if is_short \
else 'preprocessing_dsamp_workflow'
ica_dir = op.join(data_path, preproc_wf_name, 'preproc_meg_dsamp_pipeline')
Here we want to grab both the raw MEG data and the coregistration file,
thus we have to specify the search patterns for raw_file and
trans_file which are parameterized with the values defined in
template_args.
template_path = '*'
raw_file = '_session_id_*_subject_id_%s/ica/%s*ses*_*filt*ica.fif'
trans_file = '../../%s/ses-meg/meg_short/%s%s.fif' if is_short else \
'../../%s/ses-meg/meg/%s%s.fif'
field_template = dict(raw_file=raw_file, trans_file=trans_file)
template_args = dict(
raw_file=[['subject_id', 'subject_id']],
trans_file=[['subject_id', 'subject_id', "-trans"]])
datasource = create_datagrabber(ica_dir, template_path, template_args,
field_template=field_template,
infields=['subject_id'],
outfields=['raw_file', 'trans_file'])
Note
create_datagrabber() is used with different
input paramters respect to 02. Preprocess MEG data.
Event Node¶
We define the Node that encapsulates run_events_concatenate function
(see Workflow graph) and specify the inputs and outputs of the function.
concat_event = pe.Node(
Function(input_names=['list_ica_files', 'subject'],
output_names=['raw_file', 'event_file', 'fname_events_files'],
function=run_events_concatenate),
name='concat_event')
Inverse solution Node¶
Ephypype creates for us a pipeline to compute inverse solution which can be
connected to the other nodes we created.
The inverse solution pipeline is implemented by the function
create_pipeline_source_reconstruction(),
thus to instantiate this pipeline node, we pass our parameters to it.
Since we want to do source estimation in three different conditions
(famous faces, unfamiliar faces and scrambled), we provide all information
related to the events in the json file where we also specify as inverse
method dSPM.
The inverse pipeline contains three nodes that wrap the MNE Python functions that perform the source reconstruction steps. In particular, the three nodes are:
LFComputation()compute the Lead Field matrix;NoiseCovariance()computes the noise covariance matrix;InverseSolution()estimates the time series of the neural sources on a set of dipoles grid.
The input node (raw, sbj_id, trans_file and events_file)
will be specified once the different nodes are connected.
inv_sol_workflow = create_pipeline_source_reconstruction(
data_path, subjects_dir, spacing=spacing, inv_method=inv_method,
is_epoched=True, is_evoked=True, events_id=events_id, condition=condition,
t_min=t_min, t_max=t_max, all_src_space=True, parc=parc, snr=snr)
******************** {}
Morphing Node¶
The last Node we define encapsulates compute_morph_stc function.
morph_stc = pe.Node(
Function(input_names=['subject', 'conditions', 'cond_files', 'subjects_dir'], # noqa
output_names=['stc_morphed_files'],
function=compute_morph_stc),
name="morph_stc")
morph_stc.inputs.conditions = new_name_condition
morph_stc.inputs.subjects_dir = subjects_dir
Create workflow¶
Then, we can create our workflow and specify the base_dir which tells
nipype the directory in which to store the outputs.
src_estimation_wf_name = 'source_dsamp_short_reconstruction_' if is_short \
else 'source_dsamp_full_reconstruction_'
src_reconstruction_pipeline_name = src_estimation_wf_name + \
inv_method + '_' + parc.replace('.', '')
main_workflow = pe.Workflow(name=src_reconstruction_pipeline_name)
main_workflow.base_dir = data_path
Connect Nodes¶
Finally, we connect the nodes two at a time. First, we connect the
output (subject_id) of the infosource node to the input of
datasource node. So, these two nodes taken together can grab data.
main_workflow.connect(infosource, 'subject_id', datasource, 'subject_id')
We connect their outputs to the input of
(list_ica_files, subject) of Event Node.
main_workflow.connect(datasource, ('raw_file', show_files),
concat_event, 'list_ica_files')
main_workflow.connect(infosource, 'subject_id', concat_event, 'subject')
The output of infosource, datasource and concat_event are the
inputs of inv_sol_workflow, thus we connect these nodes two at time.
main_workflow.connect(infosource, ('subject_id', show_files),
inv_sol_workflow, 'inputnode.sbj_id')
main_workflow.connect(datasource, 'trans_file',
inv_sol_workflow, 'inputnode.trans_file')
main_workflow.connect(concat_event, ('raw_file', show_files),
inv_sol_workflow, 'inputnode.raw')
main_workflow.connect(concat_event, ('event_file', show_files),
inv_sol_workflow, 'inputnode.events_file')
Finally, we connect infosource and inv_sol_workflow to
morph_stc.
main_workflow.connect(infosource, 'subject_id', morph_stc, 'subject')
main_workflow.connect(inv_sol_workflow, 'inv_solution.stc_files',
morph_stc, 'cond_files')
Run workflow¶
Now, we are now ready to execute our workflow.
main_workflow.write_graph(graph2use='colored') # colored
'/home/pasca/Science/workshop/PracticalMEEG/ds000117/derivatives/meg_derivatives/source_dsamp_full_reconstruction_dSPM_aparc/graph.png'
Workflow graph¶
Take a moment to pause and notice how the connections here correspond to how we connected the nodes.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # noqa
img = plt.imread(op.join(
data_path, src_reconstruction_pipeline_name, 'graph.png'))
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 7))
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
main_workflow.config['execution'] = {'remove_unnecessary_outputs': 'false'}
main_workflow.run(plugin='LegacyMultiProc', plugin_args={'n_procs': NJOBS})
sub-01
sub-01
['/home/pasca/Science/workshop/PracticalMEEG/ds000117/derivatives/meg_derivatives/preprocessing_dsamp_workflow/preproc_meg_dsamp_pipeline/_session_id_01_subject_id_sub-01/ica/sub-01_ses-meg_task-facerecognition_run-01_proc-sss_meg_filt_dsamp_ica.fif', '/home/pasca/Science/workshop/PracticalMEEG/ds000117/derivatives/meg_derivatives/preprocessing_dsamp_workflow/preproc_meg_dsamp_pipeline/_session_id_02_subject_id_sub-01/ica/sub-01_ses-meg_task-facerecognition_run-02_proc-sss_meg_filt_dsamp_ica.fif']
/home/pasca/Science/workshop/PracticalMEEG/ds000117/derivatives/meg_derivatives/source_dsamp_full_reconstruction_dSPM_aparc/_subject_id_sub-01/concat_event/sub-01_sss_filt_dsamp_ica-raw.fif
/home/pasca/Science/workshop/PracticalMEEG/ds000117/derivatives/meg_derivatives/source_dsamp_full_reconstruction_dSPM_aparc/_subject_id_sub-01/concat_event/sub-01_sss_filt_dsamp_ica-raw.fif
/home/pasca/Science/workshop/PracticalMEEG/ds000117/derivatives/meg_derivatives/source_dsamp_full_reconstruction_dSPM_aparc/_subject_id_sub-01/concat_event/sub-01_sss_filt_dsamp_ica-raw-eve.fif
<networkx.classes.digraph.DiGraph object at 0x7fdefa0b5b40>
Results¶
The output of this workflow is the reconstructed neural time series morphed to the standard
FreeSurfer average subject named fsaverage.The output is stored in the
workflow dir defined by base_dir. To plot the estimated source timeseries
we can use 04. Plot contrast.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 14.429 seconds)