Note
Click here to download the full example code
Compute Graph properties from a given connectivity matrix with BCT toolbox¶
The _inv_ts_to_bct_graph pipeline performs spectral connectivity over time
series, and an example wrap of a function from the
Brain Connectivity Toolbox
as an
alternative to the Radatools toolbox for graph metric computation.
This workflow makes use of two chained pipelines, and requires both graphpype AND ephypype to be installed.
The input data should be a time series matrix in npy format.
# Authors: David Meunier <david_meunier_79@hotmail.fr>
# License: BSD (3-clause)
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
import os.path as op
import nipype.pipeline.engine as pe
import nipype.interfaces.io as nio
from ephypype.nodes import create_iterator
from ephypype.nodes import get_frequency_band
Check if data are available
from graphpype.utils_tests import load_test_data
data_path = load_test_data("data_inv_ts")
First, we create our workflow and specify the base_dir which tells nipype the directory in which to store the outputs.
# workflow directory within the `base_dir`
graph_analysis_name = 'inv_ts_to_graph_analysis'
main_workflow = pe.Workflow(name=graph_analysis_name)
main_workflow.base_dir = data_path
We now use a json file for describing the connectivity parameters, loaded from a json as a dictionnary
import json # noqa
import pprint # noqa
data_con = json.load(open(op.join(op.dirname("__file__"),
"params_connectivity.json")))
pprint.pprint({'connectivity parameters': data_con})
freq_band_names = data_con['freq_band_names']
freq_bands = data_con['freq_bands']
# spectral_connectivity_parameters
con_method = data_con['con_method']
epoch_window_length = data_con['epoch_window_length']
# sampling frequency
sfreq = data_con['sfreq'] # When starting from raw MEG
# (.fif) data, can be directly extracted from the file info
frequency_node = get_frequency_band(freq_band_names, freq_bands)
Out:
{'connectivity parameters': {'con_method': 'coh',
'epoch_window_length': 3.0,
'freq_band_names': ['alpha', 'beta'],
'freq_bands': [[8, 12], [13, 29]],
'sfreq': 2400}}
Then we create a node to pass input filenames to DataGrabber from nipype
subject_ids = ['sub-0003'] # 'sub-0004', 'sub-0006'
infosource = create_iterator(['subject_id', 'freq_band_name'],
[subject_ids, freq_band_names])
and a node to grab data. The template_args in this node iterate upon the values in the infosource node
template_path = '*%s_task-rest_run-01_meg_0_60_raw_filt_dsamp_ica_ROI_ts.npy'
datasource = pe.Node(
interface=nio.DataGrabber(infields=['subject_id'], outfields=['ts_file']),
name='datasource')
datasource.inputs.base_directory = data_path
datasource.inputs.template = template_path
datasource.inputs.template_args = dict(ts_file=[['subject_id']])
datasource.inputs.sort_filelist = True
We then use the pipeline used in the previous example conmat_to_graph pipeline
from ephypype.pipelines import create_pipeline_time_series_to_spectral_connectivity # noqa
spectral_workflow = create_pipeline_time_series_to_spectral_connectivity(
data_path, con_method=con_method,
epoch_window_length=epoch_window_length)
Out:
$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$ Multiple trials $$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$
We now use a json file for describing the graph parameters, loaded from a json as a dictionnary
data_graph = json.load(open(op.join(op.dirname("__file__"),
"params_bct_graph.json")))
pprint.pprint({'graph parameters': data_graph})
# density of the threshold
con_den = data_graph['con_den']
from graphpype.pipelines import create_pipeline_bct_graph
graph_workflow = create_pipeline_bct_graph(
data_path, con_den=con_den)
Out:
{'graph parameters': {'con_den': 0.05}}
We then connect the nodes two at a time. We connect the output of the infosource node to the datasource node. So, these two nodes taken together can grab data.
main_workflow.connect(infosource, 'subject_id',
datasource, 'subject_id')
main_workflow.connect(infosource, 'freq_band_name',
frequency_node, 'freq_band_name')
main_workflow.connect(datasource, 'ts_file',
spectral_workflow, "inputnode.ts_file")
spectral_workflow.inputs.inputnode.sfreq = sfreq
main_workflow.connect(frequency_node, 'freq_bands',
spectral_workflow, 'inputnode.freq_band')
main_workflow.connect(spectral_workflow, 'spectral.conmat_file',
graph_workflow, "inputnode.conmat_file")
To do so, we first write the workflow graph (optional)
main_workflow.write_graph(graph2use='colored') # colored
and visualize it. Take a moment to pause and notice how the connections correspond to how we connected the nodes.
#import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # noqa
#img = plt.imread(op.join(data_path, graph_analysis_name, 'graph.png'))
#plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
#plt.imshow(img)
#plt.axis('off')
#plt.show()
Finally, we are now ready to execute our workflow.
main_workflow.config['execution'] = {'remove_unnecessary_outputs': 'false'}
main_workflow.run()
Run workflow locally on 2 CPUs in parrallel main_workflow.run(plugin=’MultiProc’, plugin_args={‘n_procs’: 2}) ###############################################################################
plotting k_core values
#from graphpype.utils_visbrain import visu_graph # noqa
#labels_file = op.join(data_path, "label_names.txt")
#coords_file = op.join(data_path, "label_centroid.txt")
##labels_file = op.join(data_path, "label_names.txt")
##coords_file = op.join(data_path, "label_centroid.txt")
#from visbrain.objects import SceneObj, BrainObj # noqa
#sc = SceneObj(size=(1500, 1500), bgcolor=(1,1,1))
#views = ["left",'top']
#for nf, freq_band_name in enumerate(freq_band_names):
#res_path = op.join(
#data_path, graph_analysis_name,
#"graph_bct_pipe",
#"_freq_band_name_"+freq_band_name+"_subject_id_sub-0003")
#node_k_file = op.join(res_path, "k_core", "coreness.npy")
#bin_mat_file = op.join(res_path, "bin_mat", "bin_mat.npy")
#for i_v,view in enumerate(views):
#b_obj = BrainObj('B1', translucent=True)
#sc.add_to_subplot(b_obj, row=nf, col = i_v, use_this_cam=True, rotate=view,
#title=("K-core nodes for {} band".format(freq_band_name)),
#title_size=14, title_bold=True, title_color='black')
#c_obj,s_obj = visu_graph(
#labels_file = labels_file, coords_file = coords_file,
##net_file = bin_mat_file)
#net_file = bin_mat_file, node_size_file=node_k_file)
#sc.add_to_subplot(c_obj, row=nf, col = i_v)
#sc.add_to_subplot(s_obj, row=nf, col = i_v)
#sc.preview()
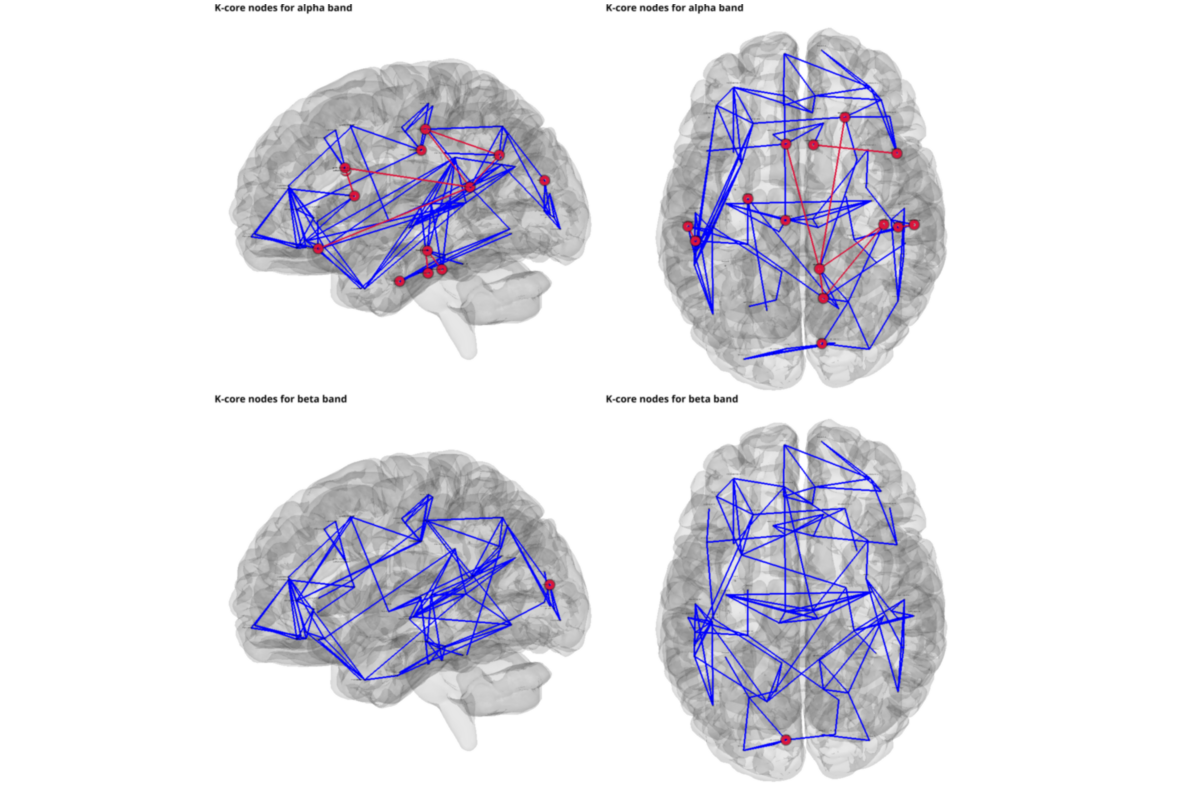
plotting k_core only
from graphpype.utils_visbrain import visu_graph_kcore # noqa
labels_file = op.join(data_path, "label_names.txt")
coords_file = op.join(data_path, "label_centroid.txt")
#labels_file = op.join(data_path, "label_names.txt")
#coords_file = op.join(data_path, "label_centroid.txt")
from visbrain.objects import SceneObj, BrainObj # noqa
sc = SceneObj(size=(1500, 1500), bgcolor=(1,1,1))
views = ["left",'top']
for nf, freq_band_name in enumerate(freq_band_names):
res_path = op.join(
data_path, graph_analysis_name,
"graph_bct_pipe",
"_freq_band_name_"+freq_band_name+"_subject_id_sub-0003")
node_k_file = op.join(res_path, "k_core", "coreness.npy")
bin_mat_file = op.join(res_path, "bin_mat", "bin_mat.npy")
for i_v,view in enumerate(views):
b_obj = BrainObj('B1', translucent=True)
sc.add_to_subplot(b_obj, row=nf, col = i_v, use_this_cam=True, rotate=view,
title=("K-core nodes for {} band".format(freq_band_name)),
title_size=14, title_bold=True, title_color='black')
c_obj,s_obj, c_obj2, s_obj2, = visu_graph_kcore(
labels_file = labels_file, coords_file = coords_file,
#net_file = bin_mat_file)
net_file = bin_mat_file, node_size_file=node_k_file)
sc.add_to_subplot(c_obj, row=nf, col = i_v)
sc.add_to_subplot(s_obj, row=nf, col = i_v)
if c_obj2:
sc.add_to_subplot(c_obj2, row=nf, col = i_v)
sc.add_to_subplot(s_obj2, row=nf, col = i_v)
sc.preview()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 5.839 seconds)